Kaolin deposit
in the Glukhovetskiy region
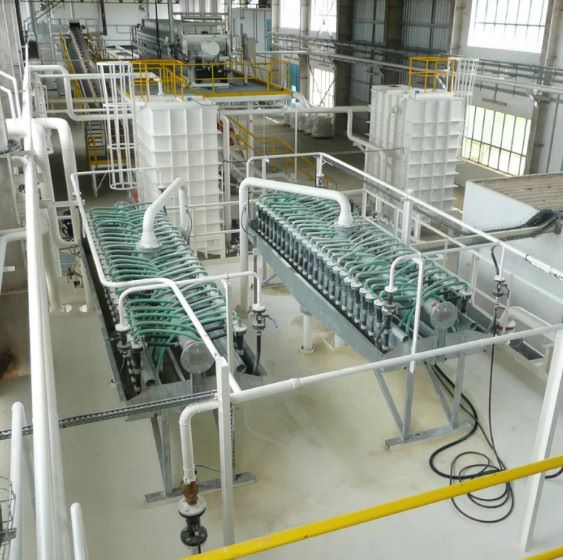
Kaolin Quang Binh Bohemia Co., Ltd. was established in 1998. QBBK is a mineral exploitation, sorting and trading unit with 100% foreign investment. The total investment capital of the project is 15,300,000 USD invested by Daily plan a.s Joint Stock Company (Czech Republic) with the most modern equipment and technology line in Europe.
Over the course of more than 25 years of operation, QBBK has grown significantly. In 2023, QBBK will invest in additional frame pressing lines, build more kaolin washing systems, increase the factory capacity to 100,000 tons/year, becoming the most prestigious unit in the Vietnamese and international markets in the field of kaolin mining, cleaning and trading.
Company Upgrades
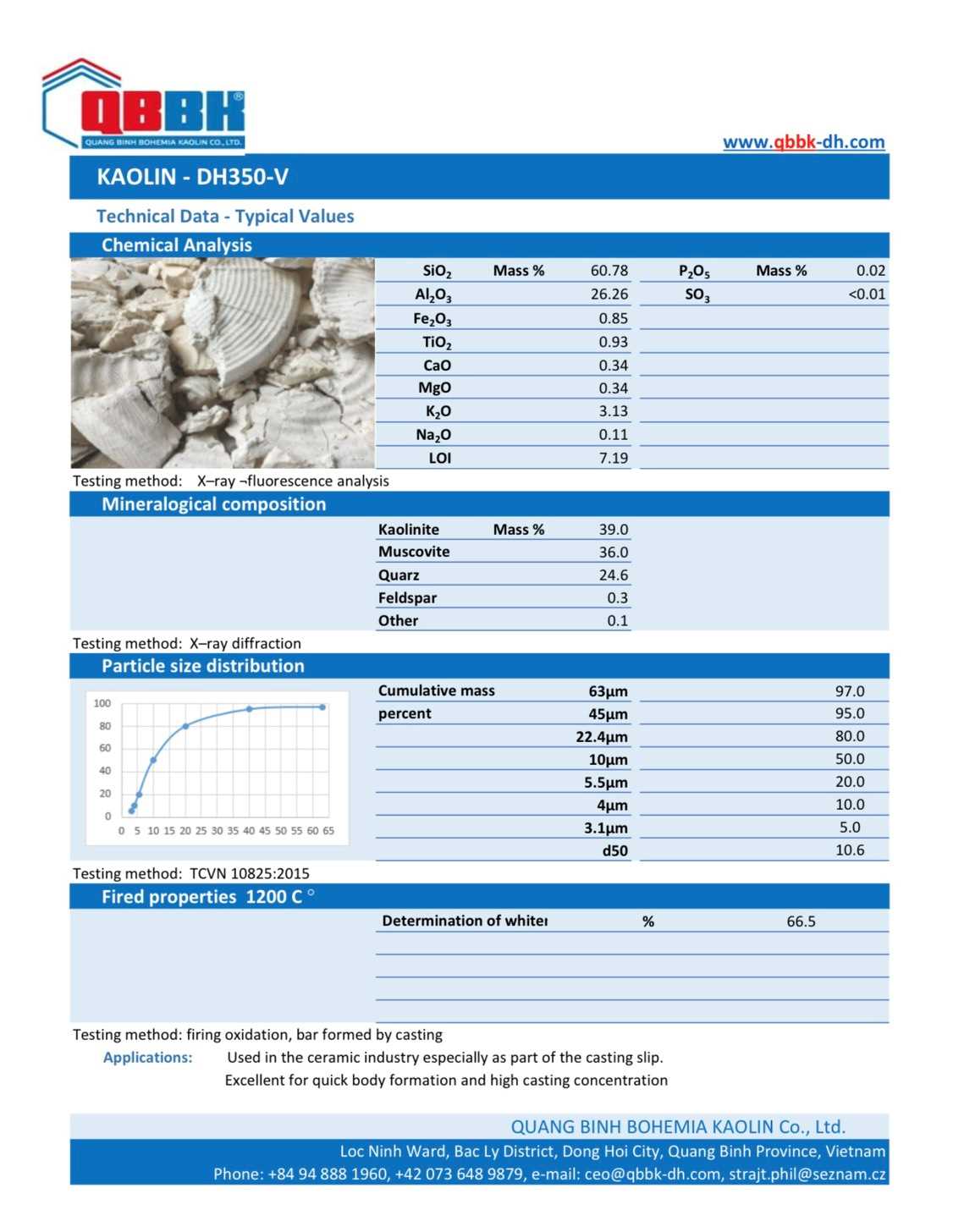
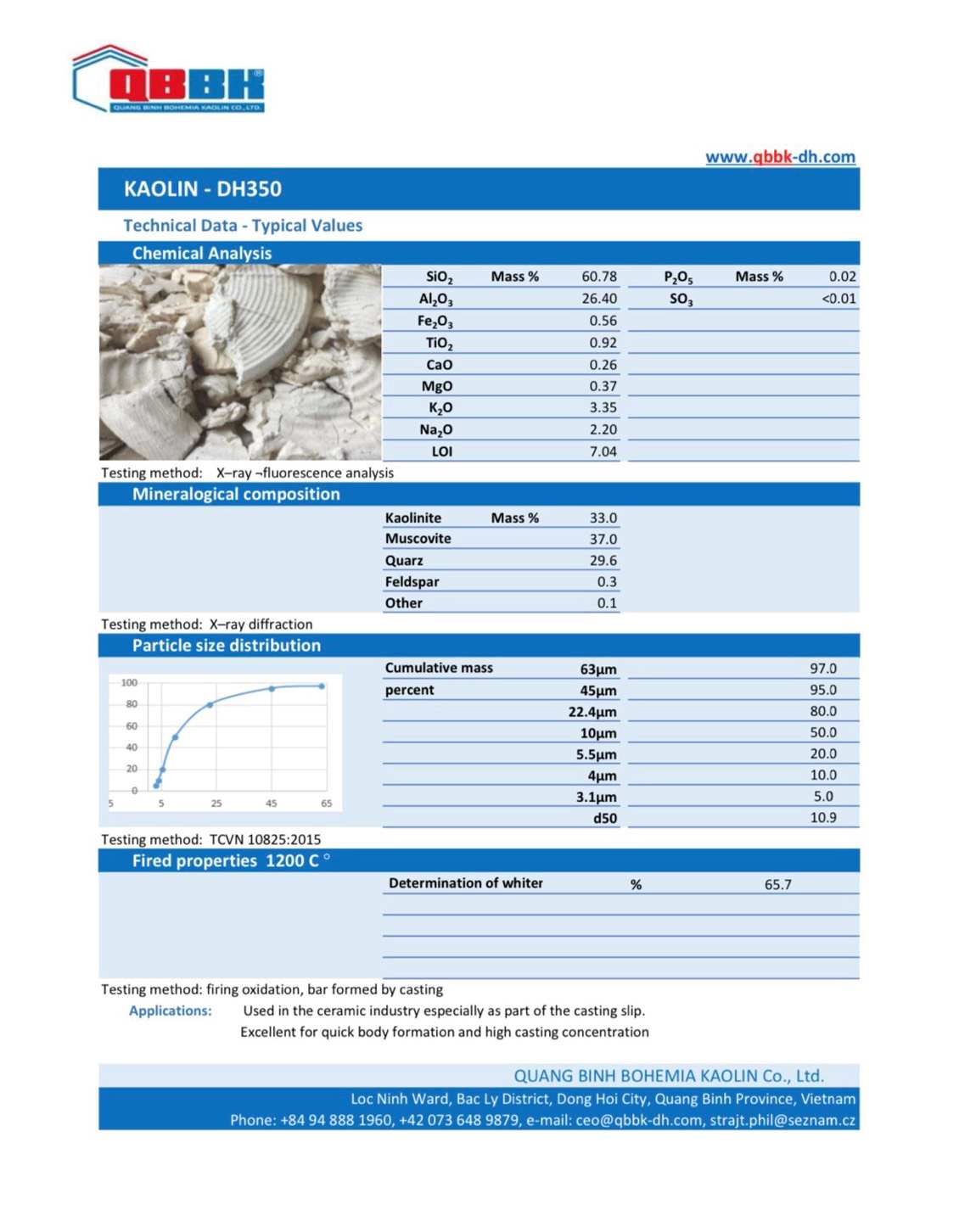
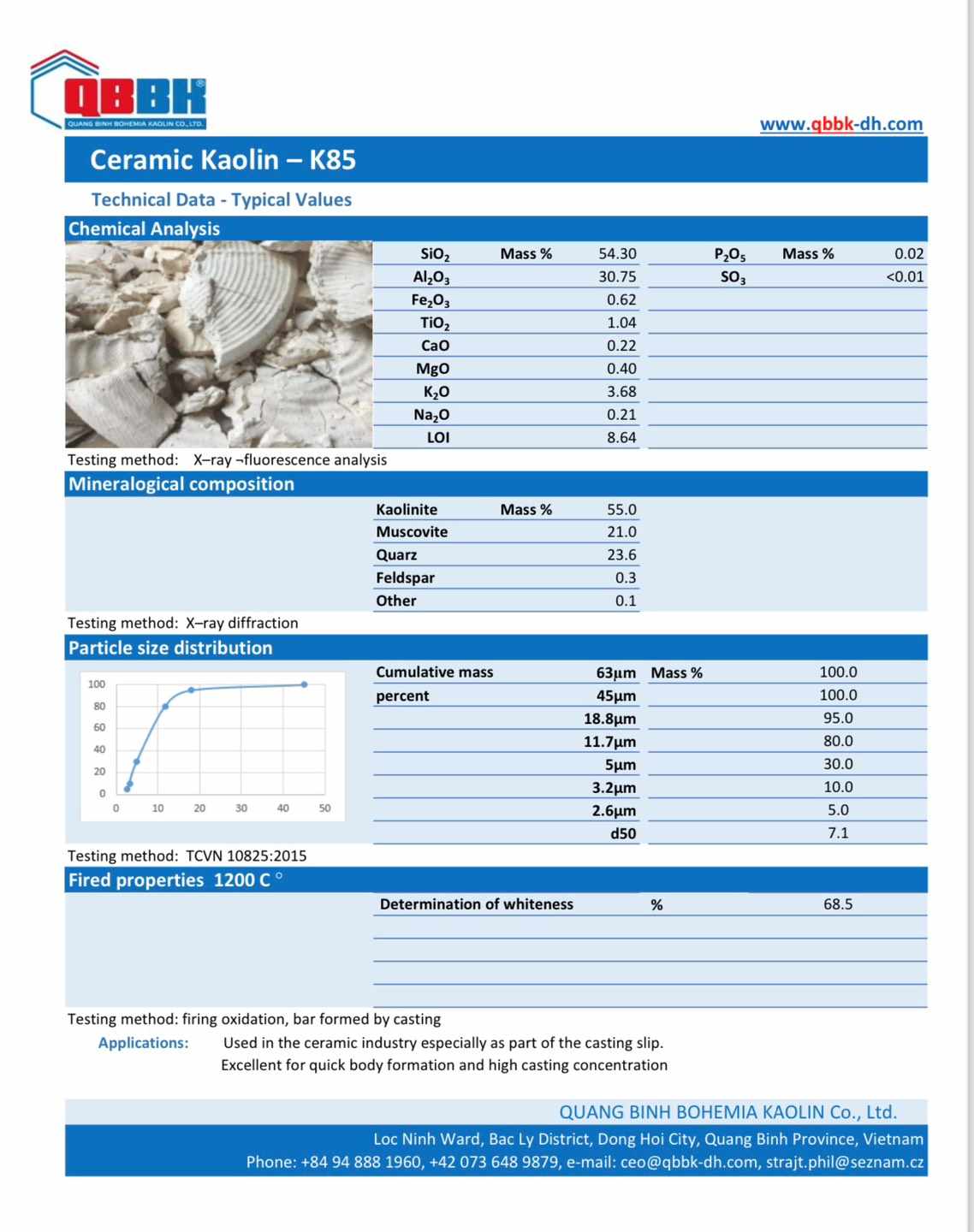
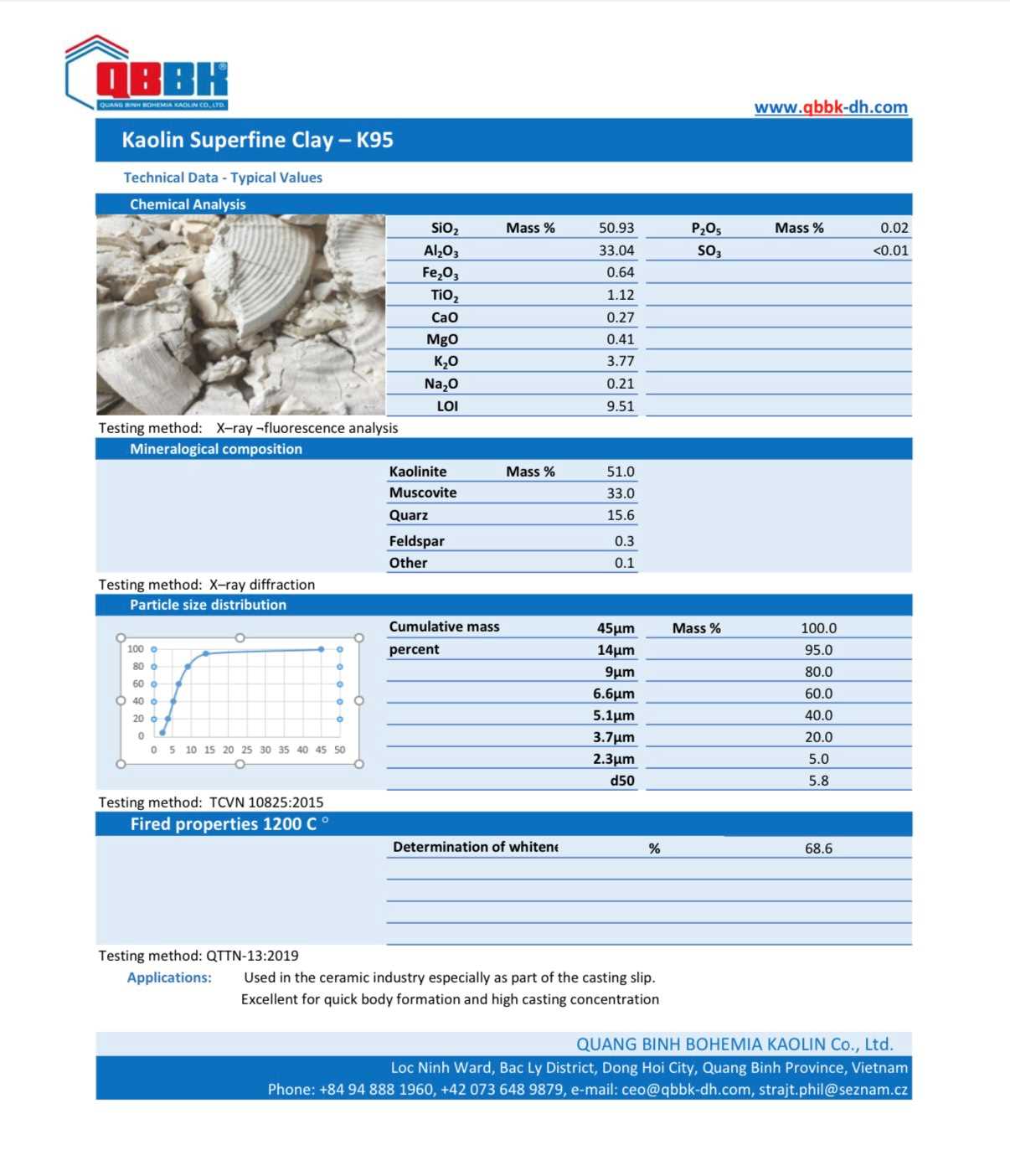
Along with that upgrade, the Company has launched more advanced product lines such as Kaolin K95, Kaolin K85 exported to Asian and European countries. Besides, it is impossible not to mention the popular products Kaolin DH350, Kaolin DH350-V, Kaolin DH500... which are still continuously supplied to domestic customers.
New brands of kaolin were created
KN-83, P2QBBK kaolin
With reserves of about 19 million tons, Bac Ly Kaolin mine, Quang Binh Province is one of the largest Kaolin mines in Vietnam (accounting for nearly 10% of national reserves) and has been approved by Quang Binh Kaolin Company Limited. Bohemia exploitation and production started in 2011.
Kaolin (kaolin) is a non-metallic mineral formed by the weathering of phenols, mainly octodaz and albite. The above weathering process is called kaolinization.
Kaolin Chemical Composition:
- Chemical formula: Al2O3.2SiO2.2H2O
- Theoretical composition: Al2O3: 39.48%; SiO2: 46.6%; H2O: 13.92%
- Density: 2.57 - 2.61
- Hardness: 1 - 2.5
- Particle size: length, width: about 0.1 - 1, thickness about 0.02 - 0.1
According to Vicnatski's concept, kaolin is aluminum-silicon acid with the formula: H2Al2SiO8H2O. When mixed with water, kaolin turns into a pasty, gelatinous mud, diluted to diffuse in H2O.
The process of decomposition from agar to kaolin
From a chemical perspective, phenpate decomposes into kaolin according to the following reaction equation:
K2O.Al2O3.6SiO2 + CO2 + H2O → Al2O3.2SiO2.2H2O + K2O3 + 4SiO2
CaO.Al2O3.6SiO2 + CO2 + H2O → Al2O3.2SiO2.2H2O + CaCO3 + 4SiO2
During the weathering process, due to the impact of CO2 and H2O, the bond between Al2O3 and SiO2 is not broken and is very stable, so the kaolin molecule is highly resistant to hydrolysis, insoluble in water, and mixed with mine wall sediments of SiO2. For alkaline earth feldspar, in addition to SiO2, CaCO3 is also mixed (if the pH of the weathering environment is less than 7, CaCO3 slowly decomposes to CaO and CO2. This CO2 is the agent that continues to weather the phenpate).